Macintosh SE
 | |
| Macintosh SE | |
| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Apple Computer, Inc. |
| Type | Personal Computer |
| Released | March 2, 1987 |
| Discontinued | October 15, 1990 |
| Intro price | US$2,898 (dual floppy) – $3,898 (with 20MB HD) |
| CPU | Motorola 68000 @ 7.8336 MHz |
| Memory | 1 MB RAM (expandable to 4 MB) |
| Storage | 800 KB or 1.44 MB floppy drive, optional 20-40 MB SCSI hard drive |
| Display | 9" monochrome CRT (512×342 pixels) |
| Sound | Monaural 8-bit, 22.254 kHz |
| Dimensions | 13.6" H × 9.6" W × 10.9" D (345 × 244 × 277 mm) |
| Weight | 17 lbs (7.7 kg) |
| OS / Firmware | System 4.0 – System 7.5.5 |
| Predecessor | Macintosh Plus |
| Successor | Macintosh SE/30, Macintosh Classic |
| Codename | PlusPlus, Aladdin, Chablis, Freeport |
| Model no. | M5010 (800K), M5011 (FDHD) |
The Macintosh SE (System Expansion) was introduced on March 2, 1987, alongside the Macintosh II. The SE added an internal expansion slot (PDS), cooling fan, support for internal SCSI hard drives, and Apple Desktop Bus (ADB) for peripherals. Configurations ranged from dual 800 KB floppy drives to combinations with 20 MB or 40 MB internal hard drives.
Model Variants
[edit | edit source]The Macintosh SE was produced from 1987 to 1990 in several configurations:
Original SE Models (1987-1989)
[edit | edit source]- Macintosh SE Dual Floppy – Two internal 800 KB floppy drives, no hard drive
- Macintosh SE 1/20 – One 800 KB floppy drive, 20 MB internal SCSI hard drive
- Macintosh SE 1/40 – One 800 KB floppy drive, 40 MB internal SCSI hard drive
Original SE models used the IWM (Integrated Woz Machine) floppy controller chip and were limited to 800 KB double-sided floppy disks.
Macintosh SE FDHD (1989-1990)
[edit | edit source]
In August 1989, Apple introduced the Macintosh SE FDHD (Floppy Disk High Density), which supported 1.44 MB high-density floppy disks. The FDHD model included:
- SWIM chip (Super Woz Integrated Machine) replacing the IWM controller
- Updated ROM (minimum System 6.0.3 required) with SWIM driver support
- Sony MPF-75W SuperDrive mechanism supporting 1.44 MB MFM-encoded disks
- Backward compatibility with 400 KB and 800 KB Macintosh disks
- PC Exchange compatibility – ability to read/write MS-DOS formatted disks
The FDHD upgrade was available as a dealer-installed kit (including ROMs, SWIM chip, and drive) for existing SE owners at US$699. In late 1989, Apple renamed the SE FDHD to Macintosh SE SuperDrive, though the hardware remained identical.
General Maintenance
[edit | edit source]Cleaning procedures, PRAM battery management, connector maintenance, and preventive care are documented in Macintosh SE General Maintenance.
PCB Schematics & Service Manual
[edit | edit source]The Macintosh SE consists of two primary circuit boards:
Logic Board
[edit | edit source]The SE logic board used two custom VLSI chips that replaced the six PAL chips from earlier models:
- BBU (Bob Bailey Unit) – VLSI custom chip for memory management
- GLU (General Logic Unit) – HAL16L8 PAL replacement handling glue logic and bus arbitration
Analog Board
[edit | edit source]The analog board provides power regulation, CRT drive circuits, and video amplification. Components include the flyback transformer, voltage regulators, and deflection circuits.
Apple Service Manual
[edit | edit source]
Service documentation is available on the Apple Service Source page.
Logic Board & Analog Board Schematics
[edit | edit source]| Logic Board | Analog Board |
|---|---|
  |
 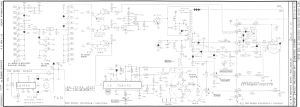 |
Capacitor Replacement Guide
[edit | edit source]Electrolytic capacitor degradation is common in SE systems. Specifications and replacement procedures are documented on the Macintosh SE Capacitor Replacement Guide page.
Retrobrite
[edit | edit source]The SE's Snow White design plastic yellows from UV exposure. Restoration techniques using hydrogen peroxide treatments are detailed on the Retrobrite page.
Troubleshooting
[edit | edit source]Simasimac patterns, Sad Mac errors, floppy drive failures, and analog board problems are covered in the Macintosh SE Troubleshooting guide.
Technical Details
[edit | edit source]System Architecture
[edit | edit source]| Sub-system | Specification (Macintosh SE, March 1987) |
|---|---|
| CPU | Motorola 68000 @ 7.8336 MHz (15.6672 MHz ÷ 2) |
| Bus width | 16-bit data • 24-bit address (16 MB addressable space) |
| ROM | 256 KB "II-class" ROM – QuickDraw 1.2, ADB support, SCSI Manager 2.0 |
| RAM | 1 MB standard (4 × 256 KB 30-pin SIMMs) – expandable to 4 MB |
| Video | 512 × 342 monochrome bitmap (21,888 bytes frame buffer) • 60.15 Hz refresh |
| Sound | 8-bit PWM DAC via VIA Port A • 22.254 kHz sample rate • monaural output |
| Storage | 800 KB Sony double-sided floppy (FDHD: 1.44 MB SuperDrive) • Optional 20/40 MB SCSI |
| I/O Ports | ADB × 2 • DB-19 ext. floppy • DB-25 SCSI • Mini-DIN-8 serial × 2 • 3.5mm audio |
| Expansion | SE PDS (Processor Direct Slot) – 96-pin Euro-DIN, full 68000 bus access |
Memory Map (Physical)
[edit | edit source]| Range | Size | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| $000000 – $3FFFFF | 4 MB | System RAM (1-4 MB populated via SIMMs) |
| $400000 – $43FFFF | 256 KB | System ROM (v5.3 for 800K, v5.5 for FDHD) |
| $580000 – $5FFFFF | 512 KB | SCSI controller space (NCR 5380) |
| $900000 – $9FFFFF | 1 MB | SCC Read (Z8530 serial controller) |
| $B00000 – $BFFFFF | 1 MB | SCC Write |
| $C00000 – $CFDFFF | ~1 MB | IWM/SWIM floppy controller |
| $D00000 – $DFFFFF | 1 MB | Expansion ROM space (PDS cards) |
| $E00000 – $E7FFFF | 512 KB | VIA space (system control) |
| $F00000 – $F8FFFF | 576 KB | Phase Read (memory timing) |
Frame buffer location: Last 21,888 bytes of installed RAM (e.g., $FF5700-$FFAFFF in 1 MB system)
ROM Versions & Features
[edit | edit source]| Version | Size | Release | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| v5.3 | 256 KB | Mar 1987 | Original SE ROM, IWM support, ADB drivers |
| v5.4 | 256 KB | Dec 1987 | Bug fixes, improved SCSI handling |
| v5.5 | 256 KB | Aug 1989 | SWIM support for FDHD, System 6.0.3+ required |
| v5.6 | 256 KB | Late 1989 | Final SE ROM, SuperDrive branding updates |
Custom Chips & ASICs
[edit | edit source]| Chip | Function | Details |
|---|---|---|
| BBU | Bob Bailey Unit | VLSI custom chip for memory control, DRAM refresh, video timing |
| GLU | General Logic Unit | HAL16L8 PAL, handles address decoding and glue logic |
| IWM/SWIM | Floppy controller | IWM (800K models) or SWIM (FDHD models) |
| NCR 5380 | SCSI controller | 8-bit asynchronous SCSI-1, programmed I/O |
| Z8530 SCC | Serial controller | Dual-channel RS-422, up to 230.4 kbps |
| 6522 VIA × 2 | System control | Timers, interrupts, sound, ADB communication |
| MC68000 | Main CPU | 7.8336 MHz, 16-bit data bus, 24-bit addressing |
SE PDS (Processor Direct Slot)
[edit | edit source]The 96-pin Euro-DIN connector provides direct access to the 68000 processor bus.
Common PDS cards:
- Radius Full Page Display – External monochrome monitor support
- Daystar Digital PowerCache – 68030 accelerator cards (16-50 MHz)
- Asanté MacCon – Ethernet networking
- Radius Accelerator 16/25 – 68020 upgrade with FPU socket
PDS Specifications:
- Full 24-bit address bus access
- 16-bit data bus
- Interrupt lines (IPL0-IPL2)
- Bus control signals (AS, DS, R/W)
- +5V, +12V, -12V power rails
- Maximum 16 MB/s theoretical bandwidth
Floppy Drive Systems
[edit | edit source]800K Drive (IWM-based)
[edit | edit source]- Sony OA-D34V-22 mechanism
- Variable speed rotation (394-590 RPM)
- GCR encoding, 80 tracks, 8-12 sectors/track
- 400 KB (single-sided) and 800 KB (double-sided) support
- IWM chip provides low-level disk control
1.44 MB SuperDrive (SWIM-based)
[edit | edit source]- Sony MPF-75W mechanism
- Constant 300 RPM rotation for HD disks
- MFM encoding for 1.44 MB capacity
- Maintains GCR support for 400/800 KB disks
- SWIM chip adds MFM encoding/decoding capability
- PC disk compatibility with appropriate software
Audio System
[edit | edit source]The SE generates sound using the classic Mac architecture:
- CPU writes 8-bit samples to VIA Port A at 22.254 kHz
- VIA Timer 1 creates PWM signal on Port B
- RC filter (R=47kΩ, C=0.01µF) smooths PWM to analog
- Optional amplification through expansion cards
- Output via internal speaker or rear 3.5mm jack
Power Specifications
[edit | edit source]- Input: 100-240V AC, 50-60 Hz (auto-switching)
- Power consumption: 100W typical, 150W maximum
- Internal voltages: +5V (logic), ±12V (drives/serial), +170V (CRT)
Environmental Specifications
[edit | edit source]- Operating temperature: 10°C to 40°C (50°F to 104°F)
- Storage temperature: -40°C to 47°C (-40°F to 116.6°F)
- Relative humidity: 5% to 95% non-condensing
FDHD Upgrade Path
[edit | edit source]Owners of original 800K SE models could upgrade to FDHD capability with:
- ROM replacement – Three ROM chips (Hi, Lo, and third ROM)
- SWIM chip installation – Replaces IWM chip at location IWM1
- SuperDrive installation – Sony MPF-75W mechanism
- System software update – Minimum System 6.0.3
The upgrade maintained backward compatibility while adding:
- 1.44 MB high-density disk support
- MS-DOS disk reading/writing capability
- Improved disk I/O performance
- Support for System 7 features
Historical Context
[edit | edit source]The Macintosh SE introduced several technical changes:
- First compact Mac with internal expansion – PDS slot for accelerators and video cards
- First compact Mac with a fan – Added despite Jobs' preference for fanless operation
- Last 68000-based compact Mac – Succeeded by the 68030-based SE/30
- Transition to ADB – Replaced proprietary keyboard/mouse connectors
- Introduction of Snow White design – Industrial design language used through the 1990s
Production estimates indicate approximately 1.5 million units sold worldwide.
Known Issues & Quirks
[edit | edit source]- Early fan noise complaints – December 1987 quieter fan retrofit available
- Analog board solder joints – Prone to cracking near flyback transformer
- 2-chip SIMM incompatibility – SE requires 8- or 9-chip SIMMs
- SCSI termination – Internal drives often improperly terminated
- ROM Easter Egg – Four photos of development team at address $41D89A
Maintenance Resources
[edit | edit source]- Macintosh SE General Maintenance – Cleaning and preventive care
- Macintosh SE Capacitor Replacement Guide – Capacitor specifications
- Macintosh SE Troubleshooting – Diagnostic procedures and fixes
- CRT Discharge Procedure – Safety for internal work
- Retrobrite – Case restoration techniques
Related Pages
[edit | edit source]- Macintosh Plus – Direct predecessor
- Macintosh SE/30 – Enhanced successor with 68030
- Macintosh Classic – Budget-oriented replacement
- Apple Desktop Bus – Peripheral connection standard
